















With the release of two GPT‑OSS models on August 5, 2025 – just two days ago – you can now run a state-of-the-art AI model on your desktop – no cloud, no monthly API fees, and no lock-in. While many open-weight large language models have appeared in recent years, OpenAI’s GPT‑OSS marks a pivotal moment: it’s the first time OpenAI has made models of this capability – comparable to GPT‑3.5-class systems – freely available under a truly permissive license. This is more than a technical release – it signals a shift in OpenAI’s approach to openness and accessibility. By moving beyond API-only access, OpenAI is rejoining the open-weight movement it once helped pioneer and redefining expectations for collaboration in AI development.
The Big Deal
- First Open-Weight Release Since GPT-2: OpenAI hasn’t shared model weights publicly since 2019. This release is a turning point for the AI community.
- Truly Open (with Apache 2.0): You can download the 20B model or the 120B model, use, fine-tune, and even commercialize these models – no royalties, no legal strings attached, and no need to share your own improvements if you don’t want to.
- Runs Locally: The smaller model (20B) runs on modern desktops equipped with a GPU offering at least 16–24GB of VRAM. The larger 120B model requires a single GPU with at least 60–80GB of VRAM – opening high-end development to a much wider audience.
👉 Download GPT‑OSS 20B or GPT‑OSS 120B models from Hugging Face
Why This Matters
With this release, OpenAI is giving the public access to the same kinds of models that previously powered major commercial systems – enabling users to self-host, modify, and build with advanced AI tools.
You Stay in Control: GPT‑OSS allows you to run advanced language models fully offline, keeping your data private and your workflows independent. If you work in a privacy-sensitive industry or simply value ownership, this is a significant milestone.
You Save on Costs: By deploying models locally, you skip ongoing cloud fees and unpredictable API bills. Your one-time hardware investment puts you in charge of your budget.
Hardware and Pricing: What Does It Take to Run GPT‑OSS?
Both GPT‑OSS models use MXFP4 (Mixture-of-Experts Fixed-Point 4) quantization, a custom low-bit precision format applied during pretraining. MXFP4 is a ~4.25-bit quantization scheme primarily targeting the MoE (Mixture of Experts) layers, designed to drastically reduce memory bandwidth and computational overhead without requiring post-training quantization.
MXFP4 quantization allows the 20B model to run efficiently within about 16GB of GPU memory, making it suitable for lower latency, local, or specialized use cases. Meanwhile, the 120B model, with a larger expert pool and deeper attention capacity, fits on a single 80GB GPU (such as the NVIDIA H100) thanks to the same MXFP4 quantization applied to its MoE layers.
In summary, both the 20B and 120B GPT-OSS models use MXFP4 quantization on their Mixture-of-Experts layers to reduce memory usage and improve efficiency without sacrificing accuracy.
Here are two real‑world hardware configuration examples for deploying GPT‑OSS models. Hardware prices can fluctuate by region and over time, so these are rough estimates (as of mid-2025):
1. High‑End Workstation/Server: For GPT‑OSS‑120B
- Example: Single server with an 80 GB GPU, such as an NVIDIA A100 80 GB (data center GPU)
- Typical system RAM: 128–256 GB
- Indicative purchase price (hardware only): $15,000 – $18,000 USD for the GPU; entire system with CPU, storage, and chassis likely in the $18,000 – $25,000 USD range.
- Suitable for: Teams needing long-context inference, multi-user workloads, or secure environments
- Limitations: High upfront cost, significant power and cooling requirements
2. Affordable Enthusiast/Mid‑Range Setup: For GPT‑OSS‑20B
- Example: Desktop PC with an RTX 4090 – consumer GPU offering 24 GB VRAM
- Typical system RAM: 32–64 GB
- Indicative price (hardware only): $1,500 – $2,500 USD for the GPU, total system around $2,500 – $4,000 USD
- Suitable for: Solo developers, enthusiasts, or small-scale local deployments
- Interactive Speed: With appropriate setup, the model can run interactively, often generating in the range of 20–50 tokens per second. Most prompts will receive an initial response in about 1–2 seconds. Larger prompts or higher precision formats may increase latency.
- Single-User Limitation: Memory limits generally restrict usage to one active user or session per GPU. Production workloads or multi-user environments require server-class or multi-GPU systems.
Example of a configuration that should allow the model to run smoothly
The model is capable of running on GPUs like the RTX 3070, but at the cost of slower inference performance.
Why Inference Only?
Because of the extreme computational demands of training models this large, most individuals and even many organizations will only use GPT-OSS for inference – that is, running the model to generate text or assist with tasks. Training from scratch remains out of reach without substantial resources.
Note: These configurations are for model inference only. Training such large models requires far more compute resources and is generally out of reach for most individuals or small organizations.
How Does GPT‑OSS Compare to Other Open-Weight Models?
To provide context, here’s how GPT‑OSS compares to other leading open-weight large language models. The table below highlights licensing, commercial use, hardware requirements, and the largest model size for each:
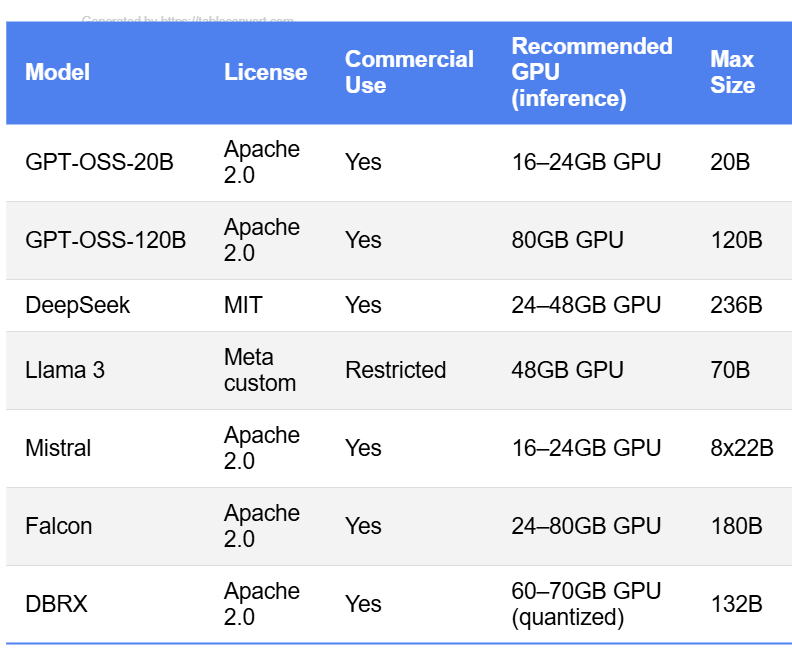
Comparison of LLMs by Licensing, Inference GPU Requirements, and the largest model available in the family
What You Can Actually Do With GPT‑OSS
- Build your own AI assistants: Create a personal chatbot, translator, or summarization tool that runs entirely on your device – even offline. Customize these solutions for your unique personal or business needs.
- Tackle enterprise challenges: Handle large volumes of documents, automate compliance, or keep confidential data secure by deploying GPT‑OSS behind your organization’s firewall.
- Build integrated developer workflows: Fine-tune GPT‑OSS on sensitive codebases or deploy models in CI/CD (continuous integration/continuous deployment) and air-gapped environments (physically isolated from the internet) – scenarios where cloud APIs can’t go. Run code review or automate developer tasks with privacy and offline capability.
- Advance your research or learning: Use GPT‑OSS to analyze literature, generate insights, or support specialized research in STEM, academia, or healthcare – all with the flexibility to adapt the model for your domain.
- Experiment, share, and contribute: Test new ideas, modify the model, and add your perspective to the growing open-weight AI community.
Limitations and Responsible Use
As with any advanced technology, there are boundaries and important responsibilities that come with using GPT‑OSS:
- Open Weights – Not Fully Open Source: GPT-OSS provides the trained model weights, but not the training data or full source code. This limits full transparency and reproducibility, and some details of the models’ inner workings remain undisclosed.
- Performance Boundaries: While GPT-OSS matches or exceeds many other open models in practical tasks, it may not reach the performance of the latest proprietary frontier models for every use case. Users should set realistic expectations and evaluate models for their needs.
- Licensing Compliance: Apache 2.0 is a permissive license, but it still requires proper attribution and has patent clauses. Anyone integrating or commercializing GPT‑OSS should review the license and ensure compliance.
- Safety and Ethics: Responsible use is essential. OpenAI encourages adherence to ethical guidelines and organizational policies. Deploy models thoughtfully, avoid harmful applications, and follow usage recommendations.
- Community Input Welcome: The open-weight AI community is evolving fast. Readers are encouraged to share feedback, discuss responsible use, and contribute ideas or best practices for deployment.
Looking Forward: A New Chapter for Open-Weight AI
With these considerations in mind, the release of GPT‑OSS opens new opportunities and challenges for developers, researchers, and organizations.
The Road Ahead: Building with OpenAI’s GPT‑OSS
OpenAI released GPT‑OSS on August 5, 2025, and the response has already energized the global AI community. Within days, major platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Cloudflare made the models accessible, enabling widespread experimentation. Early adopters – from researchers to startups – are already piloting deployments across sectors and continents, accelerating local development and open research.
This is more than a release – it’s an invitation. With access to model weights under a permissive license, developers, researchers, and organizations can now run powerful OpenAI models on their own infrastructure – without usage caps or privacy tradeoffs. Whether you’re integrating LLMs into secure environments, launching new products, or just starting to explore AI, this moment represents a rare shift in access and agency.
The bottom line: GPT‑OSS blends capability and openness in a way we haven’t seen from OpenAI before. If you’ve been waiting to build with serious AI under your own roof, now is the time to start.
Technical Resources and Downloads
Available at the official OpenAI GitHub repository
- Architecture and parameter details for both GPT‑OSS‑20B and GPT‑OSS‑120B, including MoE layer explanations, memory layout, quantization formats (like MXFP4), and inference backend support.
- Reference code, setup guides, and CLI examples for different hardware setups – from desktops to data centers.
- Direct download and install instructions via Hugging Face CLI.
- Sample integrations for Python agents, browser workflows, and developer tooling.
- Links to additional benchmarks, community integrations, and partner resources.
These materials serve as the canonical, up-to-date reference for developers, researchers, and technical users seeking to understand or extend GPT‑OSS models.
Further Reading
- OpenAI: Introducing gpt-oss
- Ars Technica: OpenAI announces two „gpt-oss“ open AI models
- Run GPT-OSS on Northflank: Deployment Guide
- How to Run GPT-OSS with Azure Container Apps
- OpenAI GPT-OSS Transformers Run Guide
- Deep Dive Analysis of GPT-OSS Models and Benchmarks
- Hugging Face Blog: Welcome GPT OSS, the new open-source model family from OpenAI!
- Business Insider: OpenAI Releases Open-Weight LLM
Disclaimer
This article was created through a process I directed from start to finish: I defined the research questions, established the article’s scope, and structured the narrative to address the most relevant technical and community concerns. AI tools – primarily ChatGPT (GPT‑4.1) for drafting and editing, and Perplexity.ai for fact-checking – were employed to support clarity and precision, but I set every editorial decision and thematic direction.
My intent in building this workflow was to blend transparent, modern research methods with strong editorial control – ensuring both high accuracy and independence from tool bias.
I’ve done my best to present the information clearly and accurately, but I know there’s always room for improvement. If you notice any errors or have suggestions for making this piece better, I’d truly appreciate your feedback.
